JavaScript
JavaScript (JS) is a lightweight, interpreted, or just-in-time compiled programming language with first-class functions. While it is most well-known as the scripting language for Web pages, many non-browser environments also use it, such as Node.js, Apache CouchDB and Adobe Acrobat. JavaScript is a prototype-based, multi-paradigm, single-threaded, dynamic language, supporting object-oriented, imperative, and declarative (e.g. functional programming) style
Last modified: May 4, 2021
The standards for JavaScript are the ECMAScript Language Specification (ECMA-262) and the ECMAScript Internationalization API specification (ECMA-402). The JavaScript documentation throughout MDN is based on the latest draft versions of ECMA-262 and ECMA-402. And in cases where some proposals for new ECMAScript features have already been implemented in browsers, documentation and examples in MDN articles may use some of those new features.
JavaScript is a scripting or programming language that allows you to implement complex features on web pages — every time a web page does more than just sit there and display static information for you to look at — displaying timely content updates, interactive maps, animated 2D/3D graphics, scrolling video jukeboxes, etc. — you can bet that JavaScript is probably involved. It is the third layer of the layer cake of standard web technologies, two of which (HTML and CSS) we have covered in much more detail in other parts of the Learning Area.
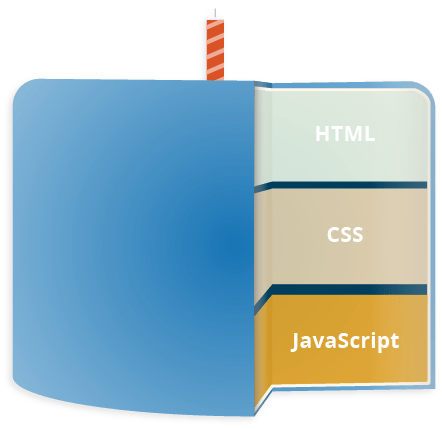
- HTML is the markup language that we use to structure and give meaning to our web content, for example defining paragraphs, headings, and data tables, or embedding images and videos in the page.
- CSS is a language of style rules that we use to apply styling to our HTML content, for example setting background colors and fonts, and laying out our content in multiple columns.
- JavaScript is a scripting language that enables you to create dynamically updating content, control multimedia, animate images, and pretty much everything else. (Okay, not everything, but it is amazing what you can achieve with a few lines of JavaScript code.)